by Maryanne Demasi, Brownstone:
 The recent findings of DNA fragments in the Pfizer and Moderna Covid-19 vaccines has led many to question why the FDA, which is responsible for monitoring the quality and safety of the vaccines, has failed to sound the alarm.
The recent findings of DNA fragments in the Pfizer and Moderna Covid-19 vaccines has led many to question why the FDA, which is responsible for monitoring the quality and safety of the vaccines, has failed to sound the alarm.
For years, the FDA has known about the risk posed by residual DNA in vaccines. Its own guidance to industry states:
TRUTH LIVES on at https://sgtreport.tv/
“Residual DNA might be a risk to your final product because of oncogenic and/or infectivity potential. There are several potential mechanisms by which residual DNA could be oncogenic, including the integration and expression of encoded oncogenes or insertional mutagenesis following DNA integration.”
Put simply, the FDA acknowledges the possibility that fragments of DNA left over by the manufacturing process can be incorporated into a patient’s own DNA, to potentially cause cancer.
FDA and WHO guidelines consider the amount of residual DNA in a single dose of traditional vaccine should not exceed 10 ng (one billionth of a gram).
But this limit – used for traditional vaccines – is unlikely to be relevant to the mRNA vaccines whose lipid nanoparticles can penetrate inside cells to deliver the mRNA efficiently.
A recent preprint paper by Speicher et al analysed batches of the monovalent and bivalent mRNA vaccines in Canada.
The authors found “the presence of billions to hundreds of billions of DNA molecules per dose in these vaccines. Using fluorometry all vaccines exceed the guidelines for residual DNA set by FDA and WHO of 10 ng/dose.”
Speicher et al also reported finding fragments of DNA larger than 200 base pairs (a measure of the length of the DNA) which also exceeds FDA guidelines.
Notably, the authors commented that for the Pfizer product, the higher the level of DNA fragments found in the vaccine, the higher the rate of serious adverse events.
Some experts say the risk of genome integration in humans is very low, but a recent publication in Nature found that around 7 percent of cells are integrated when mixed with a transfection solution containing linear pieces of DNA.
Is the FDA Concerned?
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) continues to insist that any residual DNA contamination in the Covid vaccines is not a problem and that it “stands behind its findings of quality, safety, and efficacy for the mRNA vaccines.”
“While concerns have been raised previously as theoretical issues, available scientific evidence supports the conclusion that the minute amounts of residual DNA do not cause cancer, or changes to a person’s genetic code,” added the FDA.
The FDA would not provide the “available scientific evidence” to support its claim, but it’s worth noting that the vaccines’ own product labels show that genotoxicity and carcinogenicity tests were not carried out prior to their use.
David Wiseman, a research bioscientist involved in medical product development and co-author on the study by Speicher et al said the FDA’s claim that there is no evidence of a cancer link is becoming “untenable.”
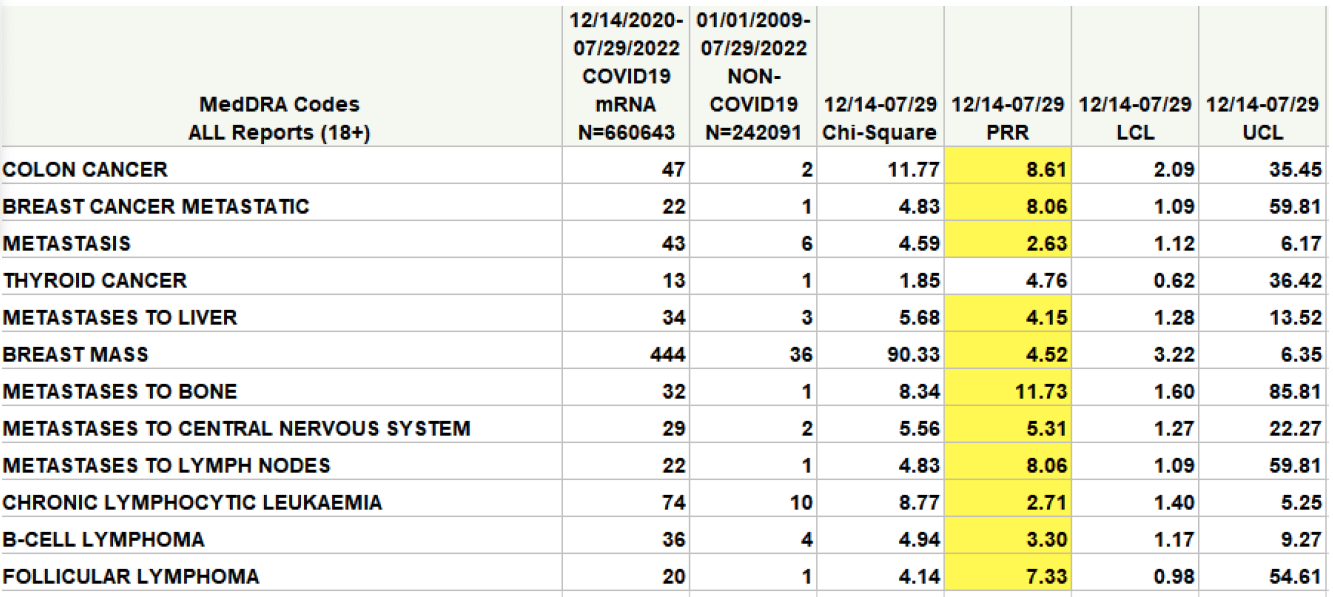
“The CDC’s own analysis on the vaccine’s safety signal in VAERS shows there could be a signal for some cancers,” said Wiseman pointing to a report he co-authored and sent to the National Academies.
In the table (highlighted in yellow), a safety signal is considered to be significant, and worthy of further investigation, if the value in the column marked PRR exceeds 2 and the value in the Chi-Square column exceeds 4.
The FDA would not confirm if it found levels of DNA that exceeded acceptable levels, nor if it was investigating further.
Instead, after months of enquiries, the FDA sent boilerplate responses to me (and other media) saying, “With over a billion doses of the mRNA vaccines administered, no safety concerns related to residual DNA have been identified.”
In response to a list of questions about its testing and oversight, the FDA said it “does not have any additional information to provide at this time.”



