from The Epoch Times:
 In this two-part paper, we aim to give an overview on COVID-19 related abnormal blood clots, how they form, how to detect them early, and how they’re being treated
In this two-part paper, we aim to give an overview on COVID-19 related abnormal blood clots, how they form, how to detect them early, and how they’re being treated
Strange Clots
Since mid-2021, unusual, lengthy blood clots found in the vessels of COVID-19 patients and jab recipients have been reported across the world.
TRUTH LIVES on at https://sgtreport.tv/
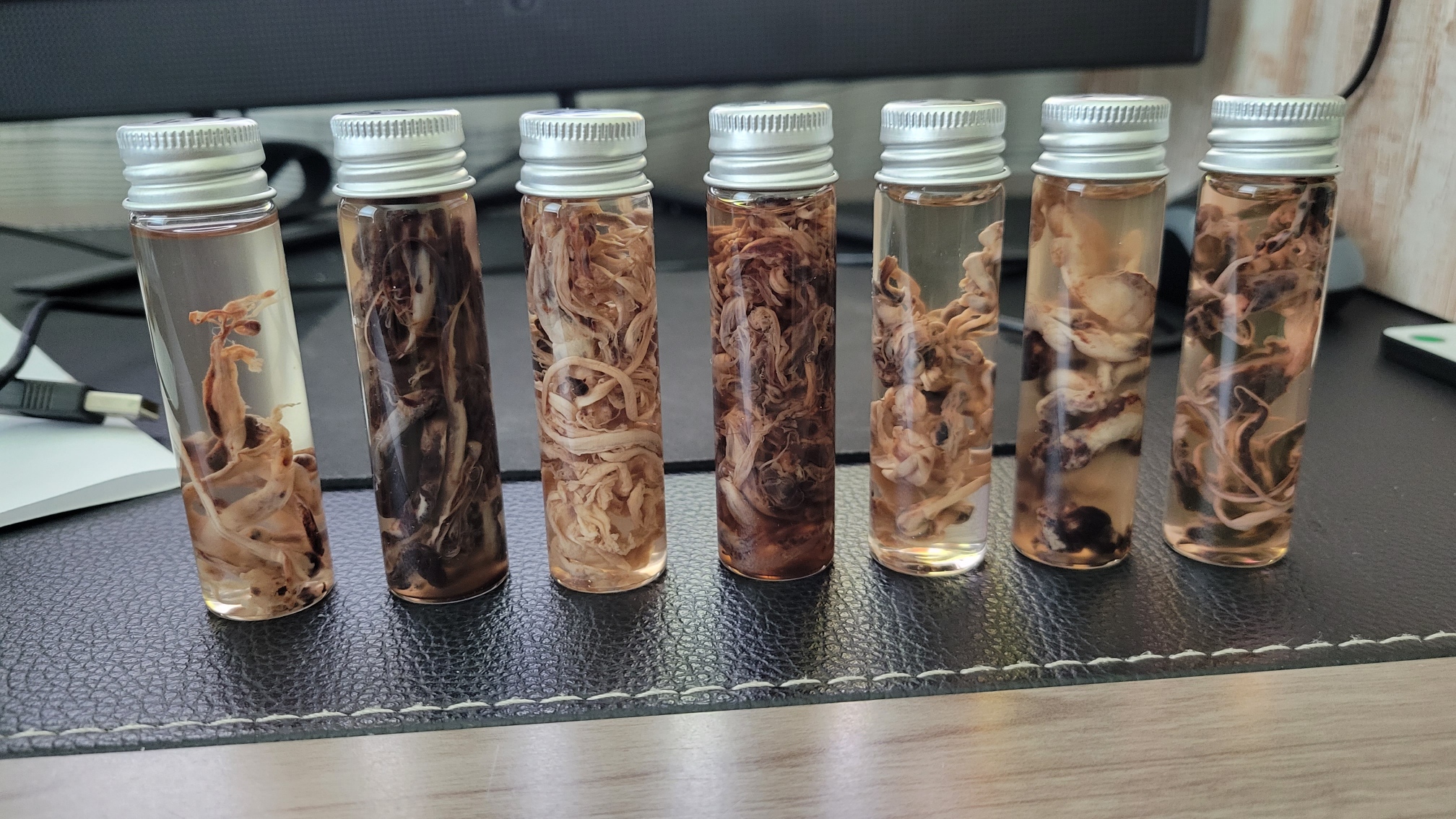

“We as embalmers are seeing some strange clots since the COVID outbreak. These clots are very rubbery feeling and very long as they exit the veins that we use during the embalming procedure. They really appear to be like earthworms. I have never seen this in my career until now,” Larry Mills, a licensed embalmer and funeral director in the State of Alabama, told The Epoch Times.
Other embalmers confirmed similar findings and spoke on the condition of anonymity.
Richard Hirschman, Alabama funeral director and embalmer since 2001, was one of the first to bring attention to this phenomenon. He said that prior to COVID perhaps 5 to 10 percent of people had these clots. Now more than half of the bodies he sees have them.
One embalmer, licensed since 2001, said in an interview, “I can tell you with certainty that the clots Richard has shown online are a phenomenon that I have not witnessed until probably the middle of last year. That is pretty much all I have to say about it. I have no knowledge as to what is causing the clots, but they did seemingly start showing up around the middle of 2021.”
Where do these strange, fibrous clots come from? How do they form?
A Condition With Over 200 Symptoms
Doctors have realized, since the early days of the pandemic, that COVID-19 is not just a lung disease, but also an endothelial and vascular disease.
Physicians have summarized a list of unusual clinical observations of COVID-19 including but not limited to severely hypoxic (low oxygen) patients despite relatively normal lung compliance upon examination, thrombotic complications, and consistent autopsy findings of blood clots (thrombi) in the microcirculation of the lung.
After an acute COVID-19 infection, over 200 different lingering symptoms have been reported for long COVID, which can persist for about 6–24 months.
This is perhaps the largest number of symptoms reported with a medical condition so far.
The most frequent symptoms include breathlessness, fatigue, brain fog, cognitive dysfunction, muscle aches and pains (myalgia), sleeping difficulties, and anxiety or depression.
The chronic, relapsing nature of long COVID is mainly caused by immune dysregulation, hyperinflammation, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial dysfunction.
But how could it be, and why? Clues have emerged since 2020.
Blood Clots Causing Symptoms
In November 2020, a report with findings of increased microclots in COVID-19 patients versus healthy or diabetic patients could reasonably explain the breathlessness, fatigue, and post-exertional malaise syndrome.
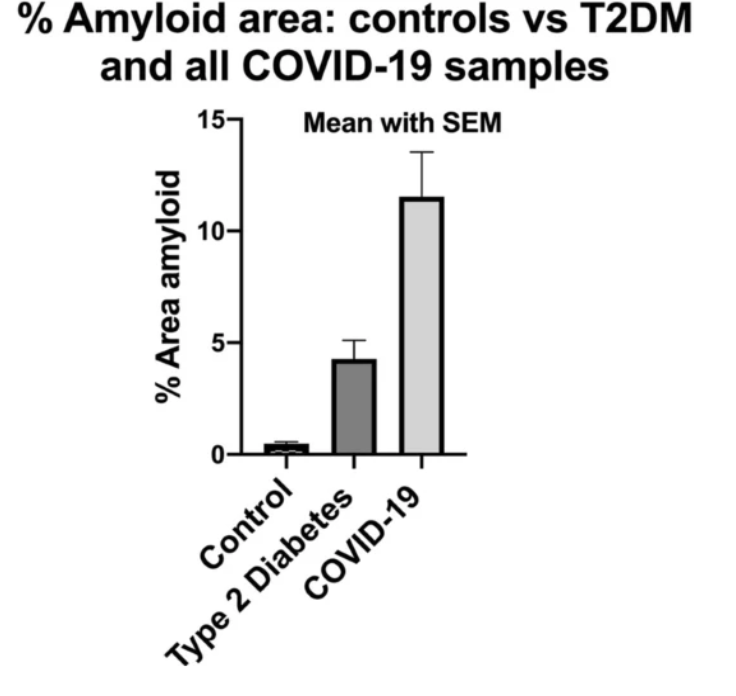
Moreover, a large scale cohort UK study based on 48 million adults in England and Wales found that in the first week after a COVID-19 diagnosis, the risk of an arterial blood clot was nearly 22 times higher than in someone without COVID-19, and 33 times higher for a venous clot condition.
An artery clot is the kind that could cause a heart attack or ischemic stroke by blocking blood flow to the heart or brain.
This has led to an estimated 10,500 additional cases of clot-related problems, i.e. about 7,200 additional heart attacks or strokes, and 3,500 additional cases of pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, or other venous problems.
Even though that risk drops sharply to less than four times higher than someone without COVID in the second week, it remains high (2x) even up to 49 weeks after the initial diagnosis. This is especially so in regards to the risk of deep vein thrombosis. These are clots that form in large veins.



